Oral Cancer

Overview
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a malignant condition that develops in the tissues of the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, floor, or roof of the mouth. Early detection is often difficult but is vital for effective treatment and improved chances of survival. Understanding oral cancer symptoms and risk factors helps facilitate timely diagnosis. Treatment approaches vary depending on the stage and location of cancer, with options including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Early intervention can significantly enhance treatment success rates, preserve vital functions, and improve overall quality of life.
Take control of your health today by recognising the signs and seeking expert evaluation without delay.
Early action can make all the difference in successful oral cancer treatment outcomes.
Book ConsultationWhat is Oral Cancer?
The oral cancer definition refers to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within the tissues of the mouth. Oral cancer begins when these cells multiply uncontrollably, potentially affecting the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, floor of the mouth, or hard palate, and may spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Understanding the types of oral cancer can help in early detection and tailored treatment approaches. Early diagnosis significantly enhances the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival.
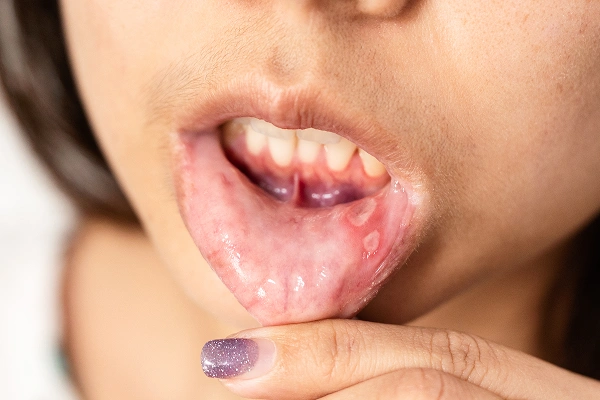
What are the Symptoms of Oral Cancer?
Recognising oral cancer symptoms early enables timely medical intervention, improving outcomes. Watch for:
- Unexplained lumps or thickening in the mouth
- Red or white patches on the tongue, gums, or mouth lining
- Oral sores or growths that bleed easily
- Pain, numbness, or tingling in the mouth or lips
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking
- Regular dental or medical check-ups are essential for early detection of these signs.
What are the Causes and Risk Factors?
Understanding the oral cancer causes and the oral cancer risk factors that contribute to it is crucial. These include lifestyle and environmental exposures such as:
Alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol intake significantly elevates risk.
HPV infection
Certain HPV strains are associated with cancers of the oral cavity.
Poor oral hygiene
Inadequate oral care can increase susceptibility to chronic irritation and disease.
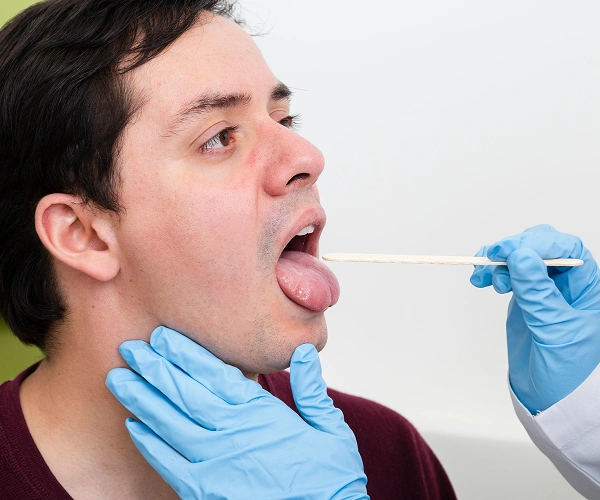
How is Oral Cancer Diagnosed?
Knowing how to detect oral cancer involves a combination of clinical evaluation and specialised testing:Knowing how to detect oral cancer involves a combination of clinical evaluation and specialised testing:
Clinical examination
Biopsy
Imaging tests
Diagnostic accuracy

How is Oral Cancer Staged?
Oral cancer stages assess how far cancer has spread and guide treatment. Understanding these stages also helps recognise potential oral cancer last stage symptoms, which may indicate advanced disease requiring more aggressive management:
Treatment Options for Oral Cancer
Understanding how to treat oral cancer begins with a customised plan based on the cancer’s stage, location, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. Treatment options include:
Oral Cancer Recovery Timeline
Preoperative Preparation
(1–2 weeks)
Evaluation, prehabilitation, and planning
Nutritional advice, mental preparation
Surgery & Hospital Stay
(Day 0–7)
Surgical tumour removal and critical monitoring
Pain management, wound care, early mobilisation
Early Recovery Phase
(1–4 weeks)
Healing, managing side effects, such as swelling and pain
Nutritional support, speech and swallowing exercises
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up
(1–3 months)
Functional rehabilitation and monitoring
Therapy coordination and lifestyle guidance
Long-Term Recovery
(3 months and beyond)
Ongoing surveillance for recurrence and restoration of oral functions
Regular check-ups and emotional support
Outcomes and Survival Rates
A frequently asked question among patients is, “Is oral cancer curable?” Oral cancer survival rate and outcomes depend on the stage at diagnosis and the timeliness of treatment. Early-stage oral cancers have higher cure rates, while advanced disease often requires combined modality treatments and close monitoring. Multidisciplinary care not only improves the chances of a cure but also enhances functional outcomes, supporting better speech, swallowing, and overall quality of life after treatment.

Dr. Amit Chakraborty
Cancer Surgeon
Why Choose Dr. Amit Chakraborty for Oral Cancer Treatment?
- Renowned expertise in both surgical and non-surgical therapies for oral cancer
- Individualised treatment planning supported by a multidisciplinary team
- Access to advanced surgical techniques, including reconstructive and minimally invasive procedures
- Committed to comprehensive patient education and compassionate care
0
Treated Cancer Patients
0
Complex Surgeries
0%
Success Rate
FAQs
Yes, early detection is possible through regular dental check-ups and awareness of symptoms.
Treatments include oral cancer surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and supportive care.
Pain varies by stage; early lesions may be painless, with pain increasing as cancer progresses.
Avoid tobacco and alcohol, maintain good oral hygiene, and protect your lips from excessive sun exposure.
Side effects include pain, swelling, fatigue, and difficulty eating or speaking; supportive therapies can alleviate these.
Regular follow-ups with clinical exams and imaging are essential, scheduled based on treatment and response.
The cost of oral cancer treatment in India varies based on the stage of cancer, the type of surgery required, and whether reconstruction or additional therapies are needed. On average, oral cancer treatment costs ₹95,000 to ₹10,00,000 in India. A detailed estimate is provided after consultation.
Together, We Can Fight Against Cancer
Contact us via phone or fill out our appointment form to schedule a consultation with Dr Amit Chakraborty.
Book Consultation