A small mouth ulcer that doesn’t hurt or a white or red patch that hasn’t changed can feel easy to ignore. Many people quietly wonder, “How long does oral cancer take to spread?”
The answer is not always alarming but it is important. Oral cancer often develops slowly over months or years, especially in early stages, though progression can be faster in some cases. It rarely spreads overnight, yet delaying evaluation for too long can limit treatment options.
Understanding how oral cancer progresses helps patients make calm, informed decisions. Early assessment often allows simpler, function-preserving treatment, protecting speech, swallowing, and quality of life without panic or pressure.
What Are The Causes of Oral Cancer?
Understanding what drives oral cancer spread starts with knowing how the disease begins. Oral cancer does not appear suddenly. It develops when the lining of the mouth faces repeated damage over time.
1. Tobacco use remains the strongest cause. Smoking or chewing tobacco injures oral cells again and again until normal repair fails.
2. Areca nut and betel quid chewing increases risk even without smoking.
3. Alcohol consumption worsens cellular injury. The risk rises sharply when alcohol combines with tobacco.
4. Chronic irritation from sharp teeth or poorly fitting dentures keeps tissues inflamed. Over time this can encourage malignant change.
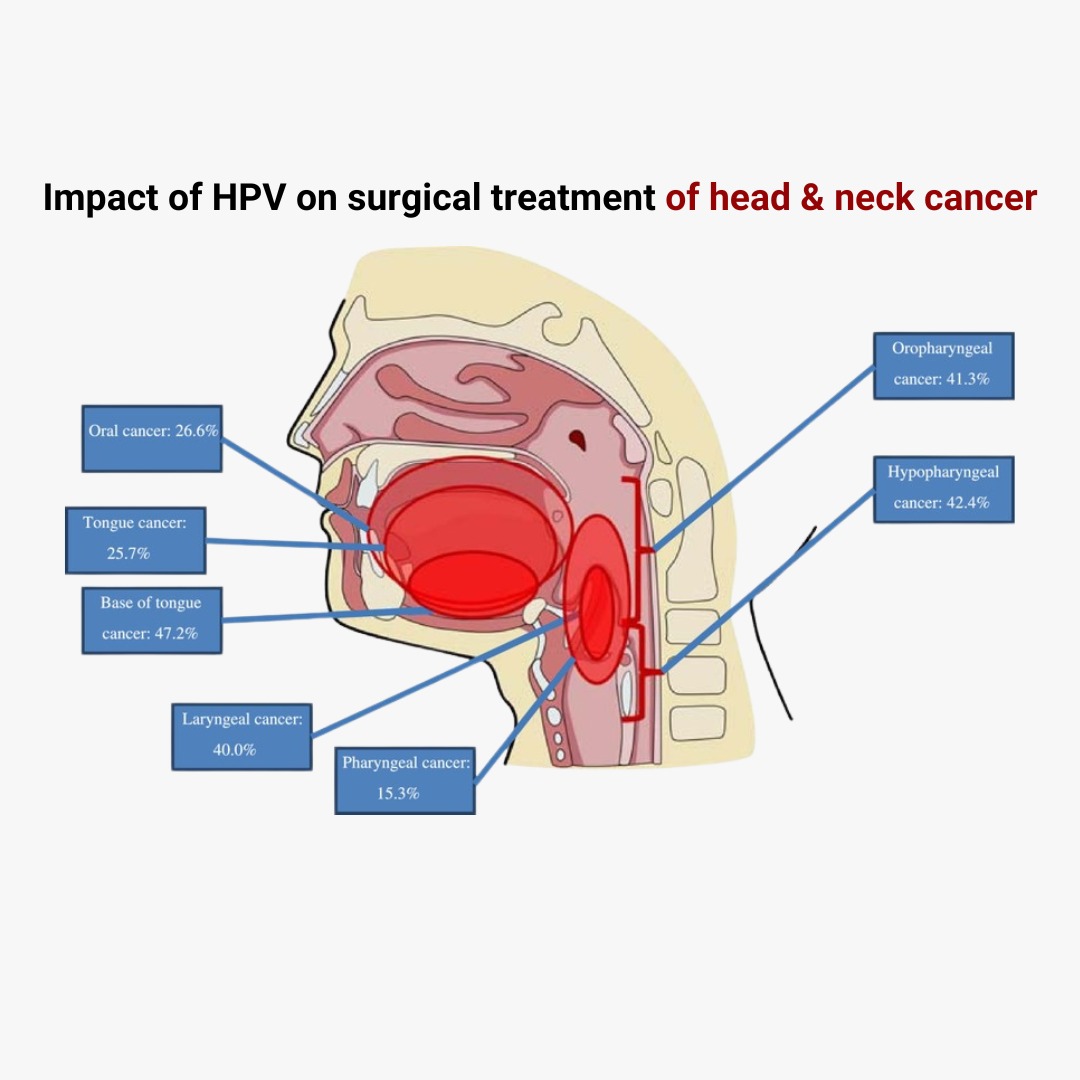
5. Human papillomavirus HPV plays a role in some oral cancers though it appears more often in throat cancers.
These causes act slowly. Damage builds over years. Early disease often looks harmless. That is why delay feels easy.
What Are The Early Warning Signs of Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer rarely announces itself loudly. It begins quietly. Many early changes feel minor and easy to dismiss.
1. A non-healing mouth ulcer is often the first sign. It stays longer than two weeks. It may not hurt.
2. White or red patches on the tongue or inside the cheek appear flat and harmless at first. They do not scrape off.
3. A small lump or thickened area develops slowly. It may feel firm but painless.
4. Unusual bleeding or numbness occurs without injury. This often surprises patients.
5. Difficulty chewing or speaking starts subtly. The change feels gradual, not sudden.
These signs do not always mean cancer. But persistence matters. When changes stay the same or slowly worsen it signals risk. Waiting feels safe. Sometimes it is not.
How Does Oral Cancer Cause Progresses to Disease?
Oral cancer follows a step-by-step progression. It does not usually move in a straight line. Understanding this timeline helps patients judge when waiting is still safe and when it becomes risky.
- Months to years: Cellular damage begins
Long-term exposure to tobacco alcohol or areca nut injures oral cells slowly. Changes remain invisible. No pain appears. - Several months: Early abnormal changes develop
Damaged cells start behaving differently. Small patches or ulcers form. They look stable. They feel harmless. - Weeks to months: Local growth increases
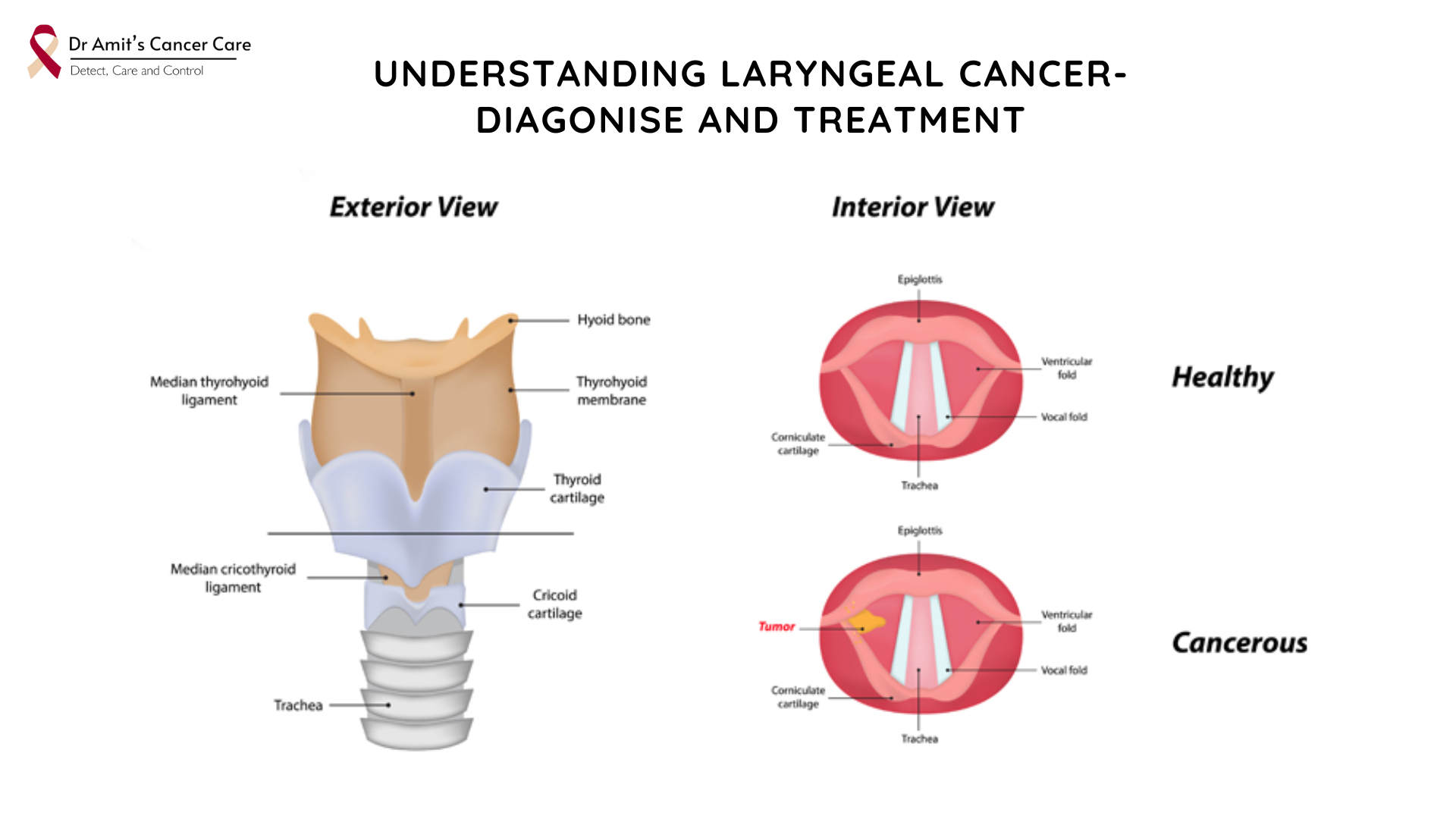
The lesion thickens or hardens. Healing stops. Spread remains limited to one area. - Months: Deeper tissue involvement
Cancer grows into muscle or bone. Treatment becomes more complex. Recovery takes longer. - Later stages: Regional spread occurs
Cancer reaches nearby lymph nodes. Treatment intensity increases. Early simplicity is lost.
Time varies for every person. Delay is the real accelerator.
What are the Prevention Measures to be followed for Oral Cancer Risk Reduction?
Oral cancer cannot always be prevented. But risk can be reduced. Timing can be improved. Outcomes can change.
- Stop tobacco and areca nut use
Quitting removes the strongest driver of disease progression. Healing capacity begins to return. - Limit alcohol intake
Alcohol magnifies damage. Reducing use lowers cumulative cellular injury. - Pay attention to persistent changes
Any ulcer patch or lump lasting more than two weeks deserves evaluation. Stability does not mean safety. - Maintain good oral health
Address sharp teeth, ill-fitting dentures and chronic irritation. Healthy tissue resists damage better. - Seek early specialist assessment
Early evaluation does not mean aggressive treatment. It often means simpler care and better preservation of speech swallowing and appearance.
Prevention is not about fear. It is about timing. Acting early keeps options open.
What are Myths and Medical Facts about Oral Cancer?
Misinformation often causes more delay than symptoms themselves. Clearing these myths helps patients act with confidence rather than fear.
- Myth: Oral cancer spreads overnight
Fact: Oral cancer usually spreads slowly. Early-stage disease often takes months or years to progress. - Myth: If it does not hurt it is not serious
Fact: Early oral cancer is often painless. Pain usually appears later. - Myth: A biopsy makes cancer spread
Fact: Biopsy does not cause cancer to spread. It enables accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. - Myth: Waiting a little longer is always safe
Fact: Time matters. Delays can allow deeper tissue or lymph node involvement. - Myth: Treatment is always disfiguring
Fact: Early detection often allows function-preserving and appearance-sparing treatment.
Facts reduce fear. Knowledge restores control.
Oral cancer does not usually spread suddenly, but it does progress steadily when ignored. Early changes often appear mild.
Time passes quietly. What begins as a small local problem can become harder to treat when evaluation is delayed. Understanding timelines removes fear and replaces it with clarity.
Early assessment helps preserve speech swallowing and appearance. It also keeps treatment simpler and recovery smoother.
The most important step is not to panic. It is awareness. When something in the mouth does not heal or keeps returning it deserves attention. Acting early protects choices. It protects quality of life.
Meet Dr. Amit Chakraborty
Head & Neck Cancer Specialist
If something about your mouth doesn’t feel right, you don’t need panic.
You need clarity.
Dr. Amit Chakraborty has spent nearly two decades doing exactly that, helping patients move from uncertainty to answers, and from diagnosis to recovery, with care that’s as precise as it is compassionate.
He is trained across India’s leading cancer institutes and the UK.
He is nationally and internationally recognised for complex head-and-neck cancer surgery.
Help Spread Awareness
Early Oral cancer symptoms are often subtle and easily missed not because they are rare, but because many people don’t know what to look for.
Sharing accurate, reliable information can help others recognise warning signs sooner and seek timely medical advice.
If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with family members, friends, or colleagues. A simple conversation or shared resource can encourage someone to pay attention to persistent symptoms and get clarity early.
Being informed empowers better health decisions. By spreading awareness, you help ensure that the people you care about are better prepared to act early, calmly, and confidently when it matters most.
If you have any further questions feel free to reach us. at +91 – 86577 17988 An early conversation is always best when it comes to our health matters.