Have you ever noticed a small sore or patch in your mouth and wondered if it meant something more? Many people see changes in their mouth and ignore them, hoping they will disappear. But early signs should not be ignored.
Oral cavity cancer is one condition that often starts with subtle changes. These changes are easy to overlook, yet they can be important to catch early. Your mouth helps you eat, speak, taste, and smile every day, so paying attention to it matters.
This blog will help you understand what the oral cavity is, what can cause cancer to develop there, and which early symptoms deserve attention.
What Is Oral Cavity?
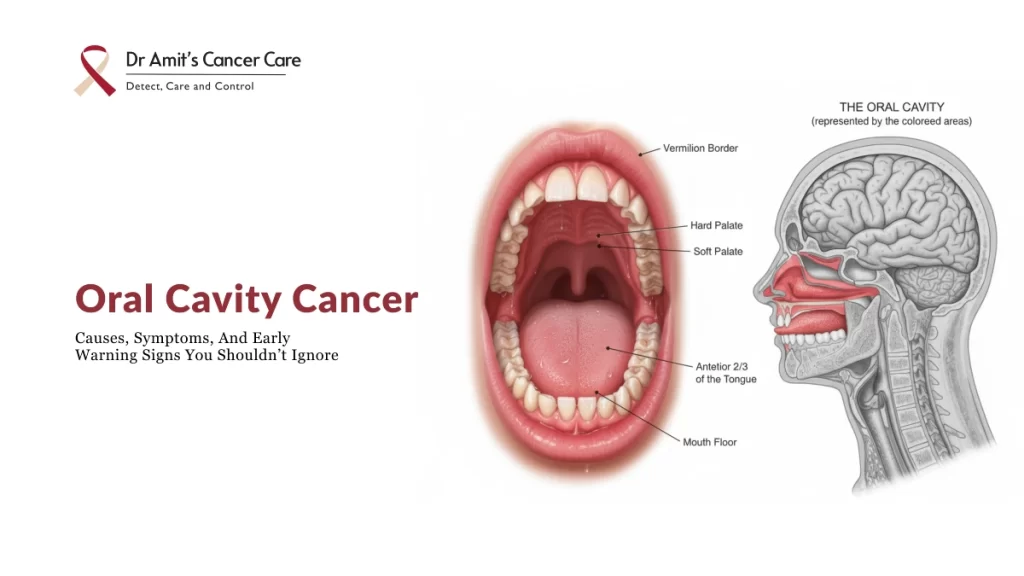
Let’s start with the basics: what is the oral cavity? The oral cavity is simply the space inside your mouth. It’s home to several important structures that help you chew food, speak clearly, taste your favourite meals, and swallow comfortably.
Your mouth works hard every single day. It’s constantly exposed to food, drinks, bacteria, smoke, and other irritants. Because of this daily exposure, the tissues in your oral cavity can sometimes become irritated or damaged over time.
The oral cavity includes these important parts:
- Lips
- Front part of the tongue
- Gums
- Inner cheeks
- Floor of the mouth (the area under your tongue)
- Hard palate (the roof of your mouth)
Understanding what the oral cavity is helps you better recognise when something isn’t quite right in your mouth.
What Is Oral Cavity Cancer?
Now that you know what the oral cavity is, let’s talk about oral cavity cancer. This type of oral cancer develops when cells in any part of your mouth begin to grow in an abnormal and uncontrolled way. Instead of growing normally and dying when they should, these cells keep multiplying, and they can form tumours.
Most oral cavity cancer cases start in the thin, flat squamous cells that line your mouth. Think of these cells as the protective covering inside your mouth. When they become cancerous, they can appear in different areas of the oral cavity, and each location may show different early warning signs.
Common places where oral cavity cancer develops:
- Tongue – especially the front two-thirds
- Lips – particularly the lower lip
- Gums – both upper and lower
- Cheeks – the inner lining
- Floor of the mouth – the area beneath your tongue
- Roof of the mouth (hard palate) – the bony front part
Here’s the good news: when doctors find oral cavity cancer early, many people recover completely and go on to live healthy, normal lives. That’s why paying attention to new sores, patches, lumps, or changes in how your mouth feels is so important. Catching the problem early means treatment works best.
What are the Causes Of Oral Cavity Cancer
Understanding oral cavity cancer causes helps you make better choices for your health. Let’s look at the main risk factors:
1. Smoking and Chewing Tobacco:
This is the biggest risk factor. If you smoke cigarettes or cigars or use chewing tobacco, your chances of getting mouth cancer are six times higher than someone who doesn’t use tobacco. The harmful chemicals in tobacco directly damage the cells in your mouth.
2. Drinking Too Much Alcohol:
Heavy drinking increases your risk significantly. When you combine heavy drinking with tobacco use, your risk shoots up even more, these two habits together are particularly dangerous.
3. HPV Infection:
The human papillomavirus (HPV), especially type 16, can cause oral cavity cancer. This is becoming more common, even in younger people who don’t smoke.
4. Too Much Sun:
Your lips can get damaged from too much sun exposure, just like your skin. People who work outdoors or spend lots of time in the sun without lip protection have a higher risk of lip cancer.
5. Age Matters:
Most people who get oral cavity cancer are over 40, though it can happen at any age.
6. Men vs. Women:
Men are twice as likely to develop mouth cancer as women, though this gap is getting smaller.
7. Poor Dental Care:
Not taking care of your teeth and gums, having dentures that don’t fit right, or having sharp teeth that constantly irritate your mouth can increase your risk.
8. What You Eat:
Not eating enough fruits and vegetables may increase your risk of oral cavity cancer.
What are the Symptoms of Oral Cavity Cancer
This is the most important part, knowing oral cavity cancer symptoms can save your life. Many of these signs are easy to spot if you know what to look for:
- Sores That Won’t Heal: If you have a sore, cut, or ulcer in your mouth that doesn’t heal within two weeks, get it checked. While most mouth sores are harmless, ones that stick around need attention.
- Strange Patches: White or red patches inside your mouth, on your gums, tongue, or cheeks can be warning signs. Red patches are especially concerning and should be checked right away.
- Lumps or Bumps: Any lump, thickening, or rough spot that wasn’t there before needs a doctor’s visit.
- Trouble Swallowing or Chewing: If it suddenly becomes painful or difficult to swallow, chew, or move your jaw, don’t ignore it.
- Numbness: Unexplained numbness or tingling anywhere in your mouth, lips, or face should be checked out.
- Sore Throat That Won’t Go Away: A sore throat that lasts more than a couple of weeks, or changes in your voice, can be oral cavity cancer symptoms.
- Ear Pain: Sometimes mouth cancer causes pain in your ear, even though your ear itself is fine.
- Loose Teeth: If your teeth suddenly become loose without any dental disease, or your dentures stop fitting properly, see your dentist.
- Can’t Move Your Tongue Easily: Difficulty moving your tongue or jaw can signal a problem.
- Unexplained Bleeding: Bleeding in your mouth without any obvious reason needs investigation.
Serious Red Flags You Must Never Ignore
When your body sends these signals, it’s important to listen.
- Any change in how your teeth fit together when you close your mouth
- Bad breath that won’t go away no matter how well you brush
- Changes in your voice that last more than two weeks
- Losing weight without trying, especially with other symptoms
- Any change in the colour or texture of your mouth tissues lasting more than two weeks
Remember: Your body is smart. When something’s wrong, it sends signals. Listen to those signals.
What Is Oral Cavity Cancer Staging?
When someone is diagnosed with oral cavity cancer, doctors need to find out how early or advanced the cancer is. This process is called oral cavity cancer staging. Staging helps doctors choose the safest and most effective treatment.
In simple terms, staging looks at three things:
- How advanced the cancer is
- Whether it has reached nearby lymph nodes
- Whether it has travelled to other parts of the body
Why staging matters for you:
- It helps your doctor decide the best treatment plan
- It gives you a better idea of what to expect during treatment
- It helps predict how well the treatment is likely to work
Stages usually range from Stage 0 to Stage IV. A lower stage means the cancer is smaller and easier to treat. A higher stage means it has spread more and may need stronger treatment. No matter the stage, your doctor will explain everything in simple language and guide you through the next steps.
How Doctors See What’s Happening
When doctors suspect oral cavity cancer, they use special imaging tests to see what’s going on inside your mouth and neck. This field is called oral cavity cancer radiology, and these pictures help doctors plan your treatment.
- X-rays: Basic dental X-rays can show if cancer has affected your jawbones or teeth.
- CT Scans: These are like super-detailed 3D X-rays that show your doctor exactly how big the tumour is and whether it’s affecting your bones or lymph nodes. CT scans are commonly used in oral cavity cancer radiology.
- MRI Scans: MRIs use magnets instead of radiation to create detailed pictures. They’re excellent for seeing soft tissues like your tongue muscles and can show how deep a tumour goes.
- PET Scans: These special scans light up cancer cells to help doctors see if cancer has spread to other parts of your body. PET scans are particularly useful for oral cavity cancer staging.
- Ultrasound: This painless test uses sound waves to look at lymph nodes in your neck.
These imaging tests might sound intimidating, but they’re painless and give your doctors crucial information to help you get better.
What Are the Treatment Options for Oral Cavity Cancer?
If you’re diagnosed with oral cavity cancer, you’ll work with a team of specialists who will create a treatment plan just for you. Oral cavity cancer treatment usually includes one or more of these approaches:
1. Surgery:
For many people, surgery to remove the cancer is the main oral cavity cancer treatment. If the cancer is small, surgery might be all you need. The surgeon removes the tumour and some healthy tissue around it to make sure all the cancer is gone. For larger cancers, you might need more extensive surgery, including removing affected lymph nodes in your neck.
Modern surgical techniques focus on removing cancer while preserving as much normal function as possible. If surgery removes a large area, plastic surgeons can often rebuild the area using tissue from other parts of your body.
2. Radiation Therapy:
This treatment uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Radiation might be used alone for small tumours or combined with surgery for larger ones. Today’s radiation techniques are much more precise, targeting cancer while protecting healthy tissue.
3. Chemotherapy:
These are powerful medicines that kill cancer cells throughout your body. Chemotherapy is often used together with radiation therapy for oral cavity cancer treatment, especially for advanced cancers.
4. Targeted Therapy:
These newer drugs attack specific parts of cancer cells. They can be effective with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy for some people.
5. Immunotherapy:
These medicines help your own immune system fight cancer. They’re showing promising results for people with advanced or recurrent oral cavity cancer.
6. Support Services:
Treatment often includes help from nutritionists (to make sure you eat well), speech therapists (to help with talking and swallowing), and dentists (to protect your oral health). Pain management and emotional support are also important parts of oral cavity cancer treatment.
Your specific treatment plan depends on your oral cavity cancer staging, where the cancer is located, and your overall health. Always ask questions if something isn’t clear; your medical team is there to help you understand every step.
Protecting Yourself: Prevention Tips
While you can’t prevent all cases, you can significantly reduce your oral cavity cancer causes and risk factors:
1. Stop Tobacco Now: This is the single most important thing you can do. If you smoke or use chewing tobacco, quitting dramatically lowers your risk. Your doctor can help you quit; don’t try to do it alone.
2. Limit Alcohol: If you drink, do so in moderation. Combining heavy drinking with tobacco is especially risky.
3. Protect Your Lips: Use lip balm with SPF 30 or higher when you’re outside. Wear a wide-brimmed hat for extra protection.
4. Eat Your Fruits and Veggies: A healthy diet rich in colourful fruits and vegetables may help protect against mouth cancer.
5. Keep Your Mouth Healthy: Brush twice daily, floss, and see your dentist regularly. Your dentist checks for oral cavity cancer symptoms during routine visits.
6. Consider HPV Vaccination: The HPV vaccine can protect against cancer-causing virus strains. Talk to your doctor about whether this is right for you or your children.
7. Check Your Mouth Monthly: Once a month, do a self-exam. Look in the mirror at all parts of your mouth. Feel for any lumps. If you see or feel anything unusual, call your dentist.
Why Regular Dental Checkups Matter
Your dentist isn’t just checking for cavities; they’re also looking for oral cavity cancer symptoms. During your exam, your dentist carefully looks at every part of your mouth, including areas you can’t easily see yourself.
If you have oral cavity cancer causes like tobacco use, heavy drinking, or HPV infection, tell your dentist. You might need more frequent screenings. Early detection through routine screenings saves lives.
Living After Treatment
A diagnosis can be scary, but remember: many people successfully beat oral cavity cancer and live full, happy lives. Treatment might temporarily affect how you eat, speak, or look, but rehabilitation specialists can help you adapt and recover.
After treatment, you’ll have regular follow-up appointments. Your doctors will check to make sure the cancer hasn’t come back and will help manage any long-term effects of treatment. These checkups are crucial, don’t skip them.
Take Action Today
Here’s what you should do right now:
- Look in Your Mouth: Do a quick self-check. Look for anything unusual.
- Make an Appointment: If you haven’t seen a dentist in the past six months, schedule a checkup.
- Talk About Risk Factors: Tell your dentist if you use tobacco, drink alcohol, or have other risk factors.
- Don’t Wait on Symptoms: If you have any oral cavity cancer symptoms lasting more than two weeks, call your doctor or dentist today, not next week, not next month.
- Share This Information: Tell your family and friends about these warning signs. You might save someone’s life.
Final Thoughts
Oral cavity cancer is serious, but it is also one of the most detectable cancers when identified early. Many symptoms are visible or easy to feel, making awareness and timely action extremely important.
A sore that does not heal, an unusual patch, or a persistent lump in the mouth should never be ignored. Understanding oral cavity cancer causes and symptoms, along with early diagnosis and proper staging, greatly improves treatment outcomes.
For those seeking expert care, Dr Amit Chakraborty is a leading oncology specialist in head and neck cancers, known for managing complex oral cancer cases with a patient-focused, multidisciplinary approach that prioritises function, appearance, and quality of life.
If something feels unusual in your mouth, trust your instincts and get it checked early. That simple step can make a life-saving difference.
Reference:
- National Cancer Institute. (2025). Cancer Stat Facts: Oral cavity and pharynx cancer. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/oralcav.html