Parotid Gland Cancer
Overview
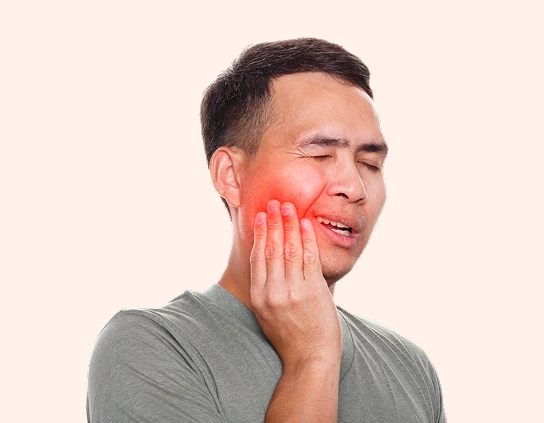
Parotid gland cancer is a rare malignancy affecting the largest salivary glands near the jaw. Common symptoms include a lump or swelling near the ear or jaw, facial numbness or weakness, pain, and difficulty swallowing. Recognising these symptoms early is vital because prompt diagnosis and intervention can lead to better outcomes. Treatment options include surgery as the primary approach, often combined with radiation therapy or, in some cases, chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Survival depends on the type and stage at diagnosis, and advances in multidisciplinary care continue to improve both recovery and quality of life for those diagnosed with parotid gland cancer.
Ready to fight against parotid cancer?
Book a consultation with Dr Amit Chakraborty for expert, personalised treatment and ongoing support.
Schedule ConsultationWhat is Parotid Gland Cancer?
The parotid gland is the largest salivary gland, located in front of and just below each ear. It produces saliva, which helps with digestion and keeps the mouth healthy.
Parotid gland cancer occurs when abnormal cells in this gland begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumour. Most parotid tumours are benign, but about 20% are cancerous. Parotid cancer can cause symptoms like a painless lump near the jaw or ear, facial weakness, pain, or difficulty moving facial muscles. Early diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and better outcomes.
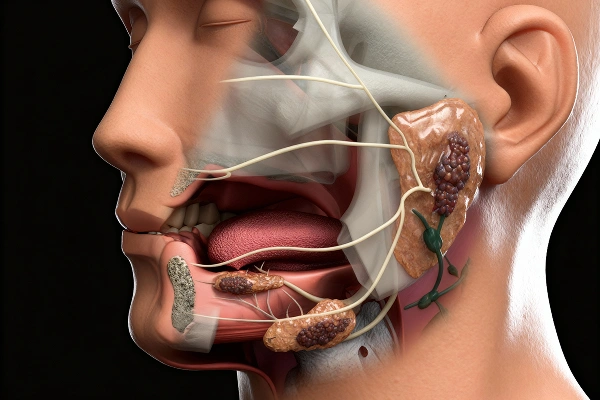
What are the Symptoms of Parotid Cancer?
Understanding the key parotid cancer symptoms is crucial, as it helps patients recognise early signs and seek timely treatment for better outcomes:
- A painless lump or swelling near the jaw, cheek, or neck
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Numbness or weakness in the face
- Difficulty swallowing or opening the mouth widely
- Facial asymmetry or drooping can signal facial nerve paralysis or involvement.
If these symptoms occur, prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional is advised.
What are the Causes and Risk Factors?
Understanding the causes and risk factors of parotid cancer is essential for early detection and prevention. The most significant evidence-based risks include:
Advanced Age
Most cases occur in individuals over 50, with risk increasing as age advances.
Radiation Exposure
Prior radiation therapy to the head or neck significantly raises the likelihood of developing parotid gland cancer.
Workplace Exposure
Prolonged exposure to substances like silica dust, nickel, rubber manufacturing byproducts, and pesticides can increase risk.
Viral Infections
Previous infection with viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, or human papillomavirus (HPV) may contribute to a higher risk.
Genetic Predisposition
Family history of cancer or a genetic tendency may increase susceptibility.
Tobacco Use
Smoking and chewing tobacco are associated with increased head and neck cancer risk, though their link to parotid cancer specifically is still being researched.
Having one or more of these risk factors does not mean parotid gland cancer will develop, but they highlight areas for screening and lifestyle adjustment.
How is Parotid Cancer Diagnosed?
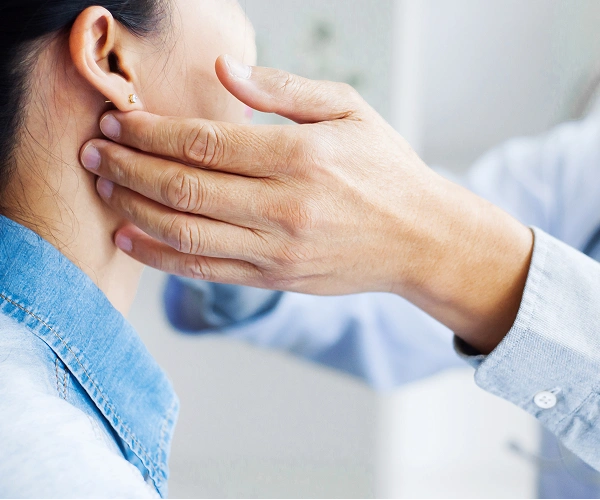
Accurate diagnosis of parotid gland cancer relies on a comprehensive combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and tissue sampling:
Physical Examination
Imaging Tests
Biopsy
Staging and Treatment Planning
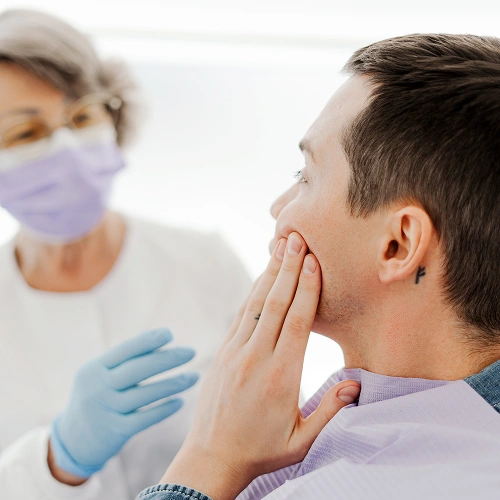
How is Parotid Gland Cancer Staged?
Parotid gland cancer staging is done using the TNM system, which reflects cancer extent:
Treatment Options for Parotid Gland Cancer
Treatment for parotid gland cancer is highly customised, based on cancer stage, type, and overall health.
Parotid Gland Cancer Recovery Timeline
Preoperative Preparation
(1–2 weeks)
Blood tests, imaging, and prehabilitation to prepare for surgery
Diet and exercise advice, surgical preparation
Surgery & Hospital
Stay (Day 0–7)
Parotidectomy performed, ICU/ward monitoring, initial pain management
Pain and wound care, early gentle activity
Early Recovery
Phase (1–3 weeks)
Parotidectomy performed, ICU/ward monitoring, initial pain management
Pain and wound care, early gentle activity
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up
(3 weeks – 3 months)
Functional therapy for speech, swallowing, and facial movement; routine follow-ups
Therapy coordination, wellness and lifestyle guidance
Long-Term Recovery & Surveillance
(3 months and beyond)
Monitoring for recurrence, managing late side effects (e.g., facial weakness, numbness)
Regular checkups, survivorship and emotional support
Outcomes and Survival Rates
Most patients regain good facial function after early treatment. Early-stage parotid cancer offers a high five-year survival rate of around 90% for localised cases, though outcomes decline with advanced disease. Overall survival varies based on tumour type, stage, and individual health factors.
Survival depends on tumour type, stage, and individual factors.

Dr. Amit Chakraborty
Cancer Surgeon
Why Choose Dr. Amit Chakraborty for Parotid Gland Cancer Treatment?
- Extensive expertise in diagnosing and treating parotid cancers
- Personalised care plans tailored to each patient's needs
- Holistic multidisciplinary support throughout treatment
- Access to advanced diagnostics and innovative therapies
0
Treated Cancer Patients
0
Complex Surgeries
0%
Success Rate
FAQs
Prognosis depends on stage and tumour type; early detection improves outcomes.
Recurrence is possible, especially in advanced stages or incomplete tumour removal.
Typically, 2–3 months, with gradual improvement in facial movement and function.
Avoid tobacco and radiation exposure to lower risk.
Risk varies by tumour location; expert surgery minimises damage and therapy supports recovery.
Regular imaging and check-ups monitor for recurrence and manage treatment effects.
The average cost of parotid gland cancer treatment in India depends on the cancer’s stage and whether surgery alone or additional treatments like radiation or chemotherapy are required. On average, parotidectomy and related treatments cost ₹70,000 to ₹2,50,000 in India. A personalised estimate is provided after medical evaluation.
Together, We Can Fight Against Cancer
Contact us via phone or fill out our appointment form to schedule a consultation with Dr Amit Chakraborty.
Book Consultation